Three Types of Patents
By: Brian Downing | Published on: 09/25/2024
This article describes the three different types of patents.
Table of Contents
1. Summary
The three types of patents are:
- Utility Patent - protects the function of an invention. When someone says "patent" they generally mean a utility patent
- Design Patent - protects the ornamental design
- Plant Patent - protects vegetation
A utility patent number will begin with a number, a design patent number will begin with a "D", and a plant patent number begin with a "P". For example, 6,285,999 is a utility patent, D82,802 is a design patent, and P5,383 is a plant patent.
2. Utility Patent
A utility patent protects the function of an invention. To be patent eligible, the invention must be a "new and useful process, machine, manufacture, or composition of matter, or any new and useful improvement thereof" [35 U.S.C. 101]. The word "patent" generally refers to a utility patent.
There are non-provisional and provisional patent applications. Only a non-provisional patent application is examined by the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) and can issue into a patent. A provisional patent application can be thought of as a one year placeholder for a non-provisional patent application.
A utility patent number begins with a number.
Example of a Utility Patent:
U.S. Patent Number 6,285,999 titled "Method for Node Ranking in a Linked Database"
Inventor: Lawrence Page
Also known as part of Google PageRank.
One of the beginning foundations of the Google empire.
3. Design Patent
A design patent protects the ornamental design of an invention. With a design patent, think of protecting the outside appearance of an invention. A design patent is not meant to protect the internal structure of an invention.
A design patent number begins with the letter D.
Example of a design patent:
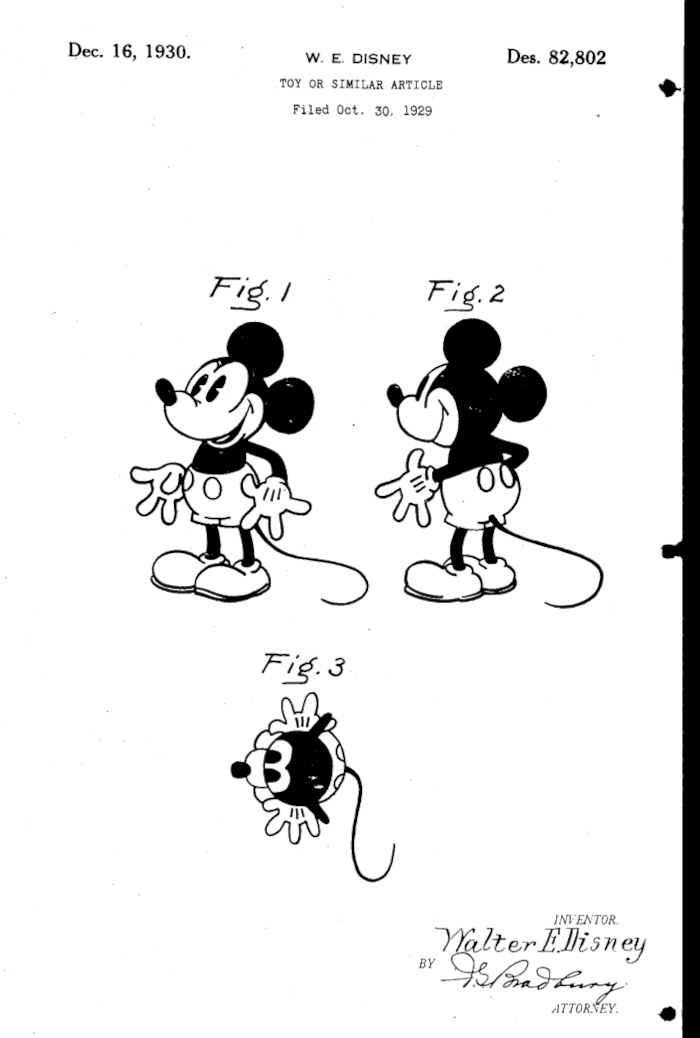
U.S. Patent Number D82,802 titled "A Design for a Toy or Similar Article"
Inventor: Walter E. Disney
4. Plant Patent
A plant patent protects vegetation. The USPTO states a "plant patent ... invented or discovered and asexually reproduced a distinct and new variety of plant, other than a tuber propagated plant or a plant found in an uncultivated state" ["General Information About 35 U.S.C. 161 Plant Patents"].
A plant patent number begins with the letter P.
Example of a plant patent:
U.S. Patent Number P5,383 titled "African Violet Plant"

